 Traditional Clothing and Attire:
Sudan's traditional dress and apparel represent the country's rich cultural legacy and ethnic
diversity. For men, the "Jalabiya" is a popular garment, frequently paired with a turban or
"Immah." Women often wear the "thobe," a bright and flowing fabric that may be draped in a
variety of ways. The "Abaya" and "Hijab" are very popular, particularly in metropolitan areas.
These traditional garments are frequently constructed of light materials suitable for Sudan's
hot environment and are embellished with elaborate embroidery and brilliant colors, showing
Sudanese textile expertise.
Traditional Clothing and Attire:
Sudan's traditional dress and apparel represent the country's rich cultural legacy and ethnic
diversity. For men, the "Jalabiya" is a popular garment, frequently paired with a turban or
"Immah." Women often wear the "thobe," a bright and flowing fabric that may be draped in a
variety of ways. The "Abaya" and "Hijab" are very popular, particularly in metropolitan areas.
These traditional garments are frequently constructed of light materials suitable for Sudan's
hot environment and are embellished with elaborate embroidery and brilliant colors, showing
Sudanese textile expertise.
 Language and Literature:
Sudan's linguistic landscape is as diverse as its culture, with Arabic serving as the official
language. However, numerous indigenous languages are spoken across the country, reflecting its
ethnic diversity. Sudanese Arabic has its unique dialect, blending standard Arabic with local
linguistic influences. In terms of literature, Sudan boasts a rich tradition of oral
storytelling, poetry, and written works. Renowned Sudanese writers like Tayeb Salih, whose novel
"Season of Migration to the North" gained international acclaim, have made significant
contributions to Arabic literature, capturing the complexities of Sudanese society and identity.
Language and Literature:
Sudan's linguistic landscape is as diverse as its culture, with Arabic serving as the official
language. However, numerous indigenous languages are spoken across the country, reflecting its
ethnic diversity. Sudanese Arabic has its unique dialect, blending standard Arabic with local
linguistic influences. In terms of literature, Sudan boasts a rich tradition of oral
storytelling, poetry, and written works. Renowned Sudanese writers like Tayeb Salih, whose novel
"Season of Migration to the North" gained international acclaim, have made significant
contributions to Arabic literature, capturing the complexities of Sudanese society and identity.
 Music and Dance:
Music and dance are fundamental to Sudanese culture, with each ethnic groups having their own
styles and customs. Traditional music frequently uses instruments such as the "Tambour" (drum),
"Rabab" (string instrument), and "Nai" (flute). Songs and rhythms are intricately linked to
daily living, social gatherings, and religious rites. Sudan's dance genres span from the
beautiful, swaying motions of Nubian dance to the frenetic "Haqibah" dances that are popular in
cities. Music and dance are not just forms of entertainment, but also significant manifestations
of community identity and legacy.
Music and Dance:
Music and dance are fundamental to Sudanese culture, with each ethnic groups having their own
styles and customs. Traditional music frequently uses instruments such as the "Tambour" (drum),
"Rabab" (string instrument), and "Nai" (flute). Songs and rhythms are intricately linked to
daily living, social gatherings, and religious rites. Sudan's dance genres span from the
beautiful, swaying motions of Nubian dance to the frenetic "Haqibah" dances that are popular in
cities. Music and dance are not just forms of entertainment, but also significant manifestations
of community identity and legacy.
 Ceremonies and Festivals:
Ceremonies and festivals in Sudan are vibrant celebrations that highlight the country's cultural
richness. Religious festivals like Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha are widely celebrated with
communal prayers, feasts, and charity. Traditional weddings are elaborate events, marked by
specific rituals, music, dance, and traditional attire. Festivals such as the "Sufi Mawlid"
celebrate the birth of Prophet Muhammad and are characterized by Sufi chanting, dancing, and
processions. Harvest festivals and local cultural fairs also provide opportunities for
communities to come together, showcasing their unique traditions, crafts, and culinary delights
Ceremonies and Festivals:
Ceremonies and festivals in Sudan are vibrant celebrations that highlight the country's cultural
richness. Religious festivals like Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha are widely celebrated with
communal prayers, feasts, and charity. Traditional weddings are elaborate events, marked by
specific rituals, music, dance, and traditional attire. Festivals such as the "Sufi Mawlid"
celebrate the birth of Prophet Muhammad and are characterized by Sufi chanting, dancing, and
processions. Harvest festivals and local cultural fairs also provide opportunities for
communities to come together, showcasing their unique traditions, crafts, and culinary delights

Sudan Clothing
Traditional Sudanese clothing reflects the country's cultural diversity and its adaptation to
the hot, arid climate. Men often wear the "jalabiya," a long, loose-fitting robe made of light
fabric, typically white or pastel-colored. This is usually accompanied by a "taqiya" (a small
skullcap) or a "turban" for headwear.
Women’s traditional attire includes the "thobe" or "toub," a large, colorful piece of cloth that
is wrapped around the body and draped over the head. The thobe comes in various colors and
patterns, often signifying different social statuses, occasions, or regions. Younger women might
also wear "zar" or "dira," which are elegant, brightly colored dresses.
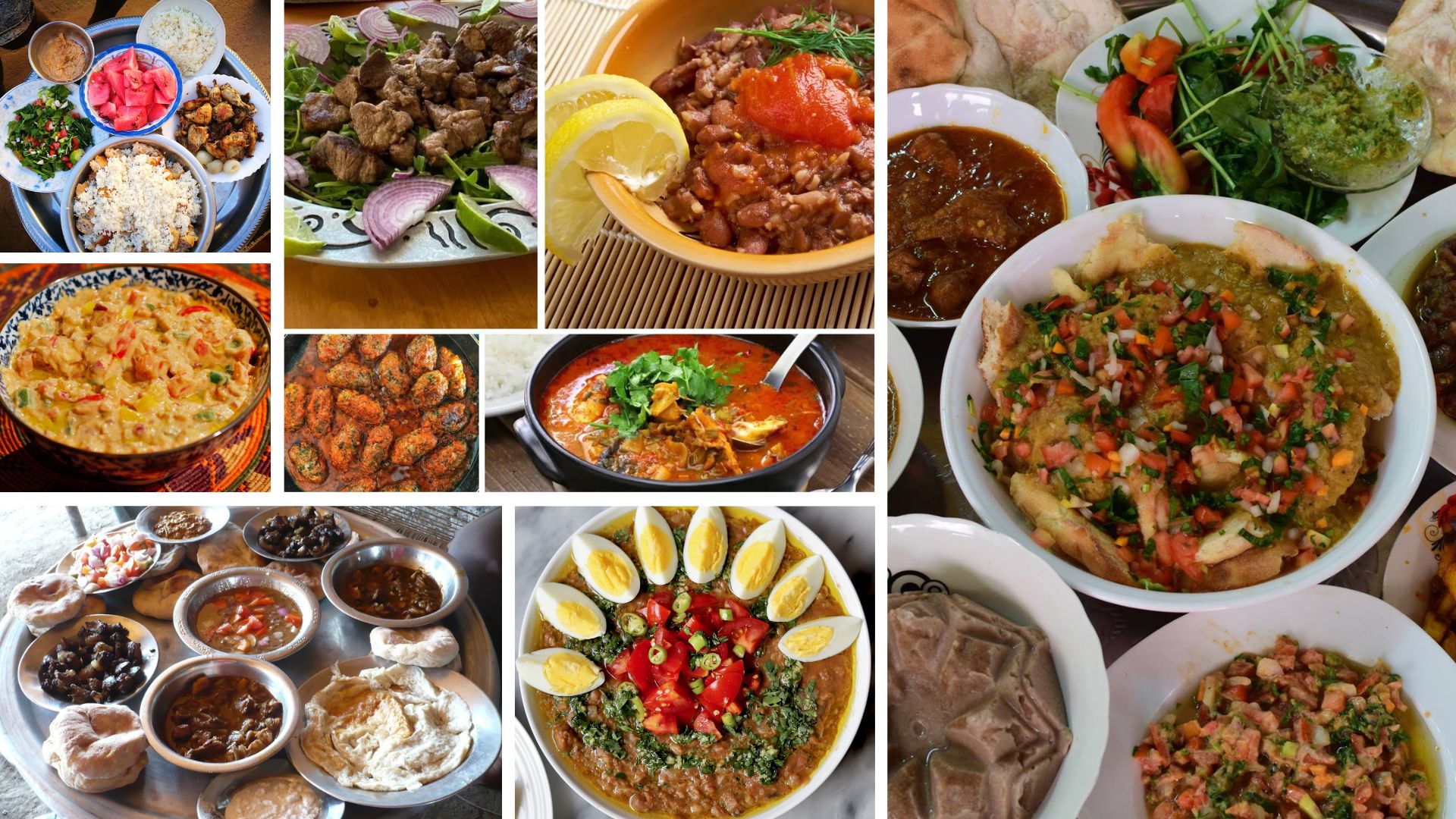

Sudan Food
Sudanese cuisine is a delightful blend of African, Arab, and Mediterranean influences. Staple
foods include sorghum, millet, and wheat, which are used to make dishes like "kisra" (a type of
flatbread) and "aseeda" (a porridge-like dish).
One of the most popular dishes is "ful medames," a hearty meal made from fava beans, seasoned
with cumin, and often topped with olive oil, lemon juice, and chopped vegetables. Another staple
is "mullah," a stew typically made with okra, meat, or fish, served with kisra or aseeda.
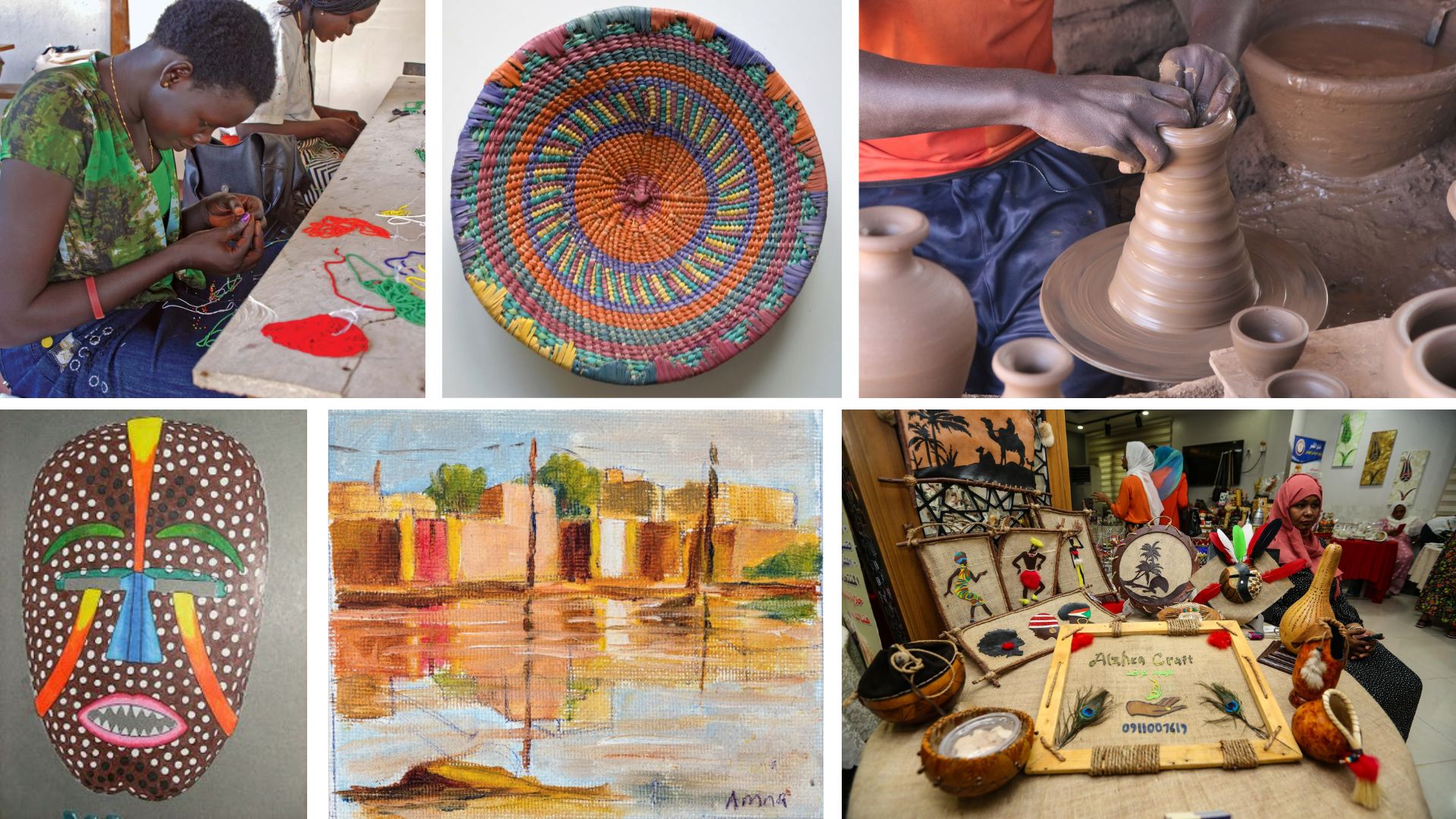

Sudan Arts and Crafts
The arts and crafts of Sudan are deeply rooted in the country's cultural history. Traditional
crafts include pottery, weaving, and basketry, with each region having its unique styles and
techniques. For example, Nubian pottery is renowned for its distinctive black and red designs,
often featuring intricate geometric patterns.
Textile arts, particularly those involving intricate embroidery, are highly valued. Sudanese
women often create beautifully embroidered garments and household items, showcasing their skills
and creativity. "Ghaba," a type of handwoven cloth, is another notable craft, often used to make
clothing and ceremonial items.
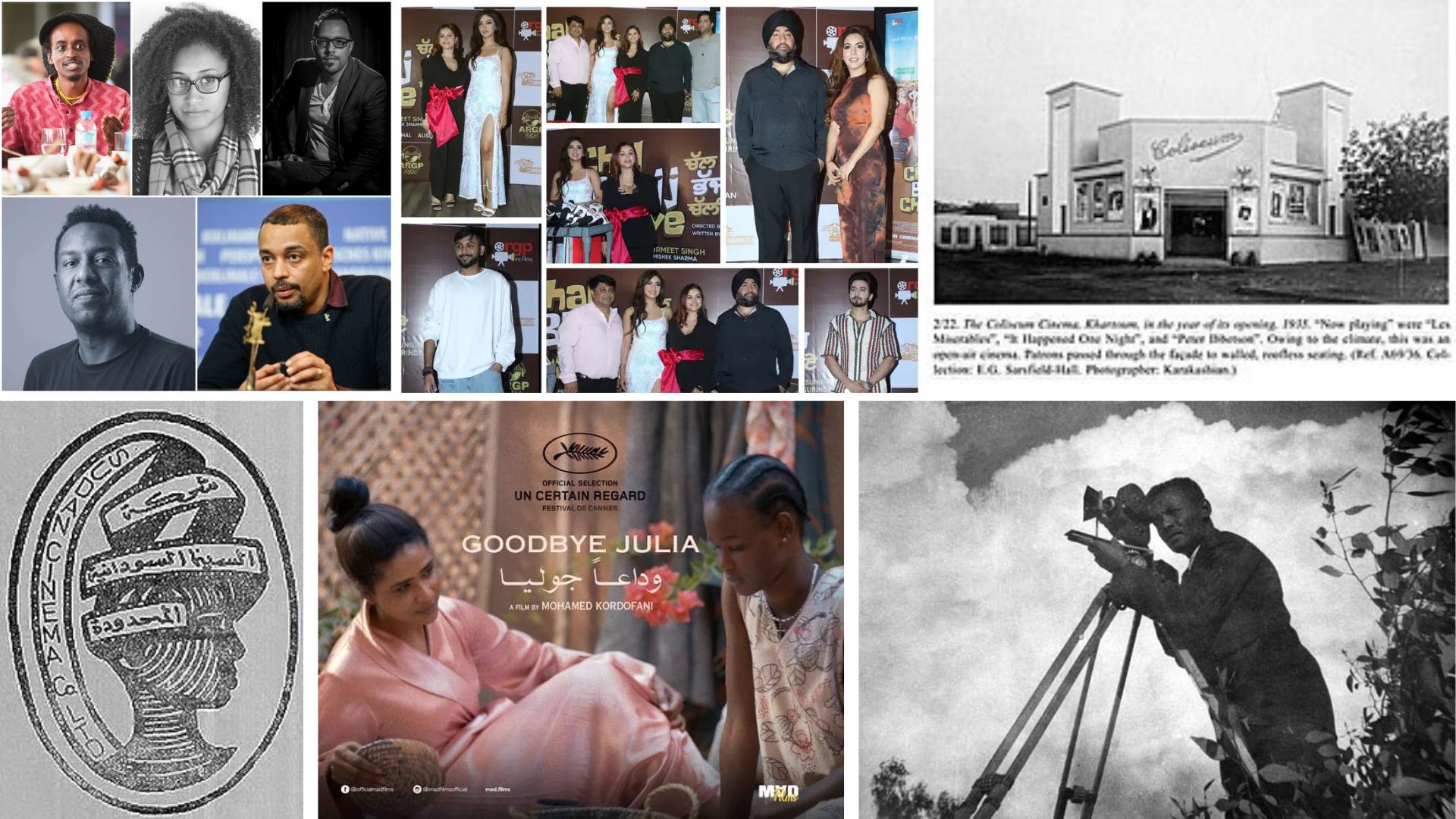
Sudan Film Industry
The Sudanese film industry, although not as prominent as in some other African countries, has a
growing presence. Historically, political instability and economic challenges hindered the
development of a robust film industry. However, recent years have seen a resurgence of interest
in filmmaking, driven by a new generation of Sudanese filmmakers.
Documentaries are a significant genre in Sudanese cinema, often highlighting social and
political issues. Notable works include "Talking About Trees," a documentary that follows a
group of veteran Sudanese filmmakers as they strive to revive cinema in their country. The film
has received international acclaim and brought attention to the challenges and aspirations of
Sudanese filmmakers.
Sudan Economy
The economy of Sudan is predominantly based on agriculture, which employs a significant
portion of the population. Major agricultural products include sorghum, millet, wheat, and
livestock. The Nile River plays a crucial role in irrigation and sustenance of agricultural
activities.
In recent years, the discovery of oil reserves has significantly impacted the Sudanese
economy, providing a vital source of revenue. However, the secession of South Sudan in 2011,
which held a substantial portion of the oil fields, led to economic challenges and
necessitated diversification efforts.
Textile and Garment Industry, Mining, Telecommunications
Tourism, Financial Services, Manufacturing, Agriculture, Renewable Energy.